How All of Russian TV Became State-Controlled
Short biography of the freedom that never happened.


Kursk was a of the Russian Navy. Its construction began in 1990 and was finished despite the collapse of the Soviet Union.
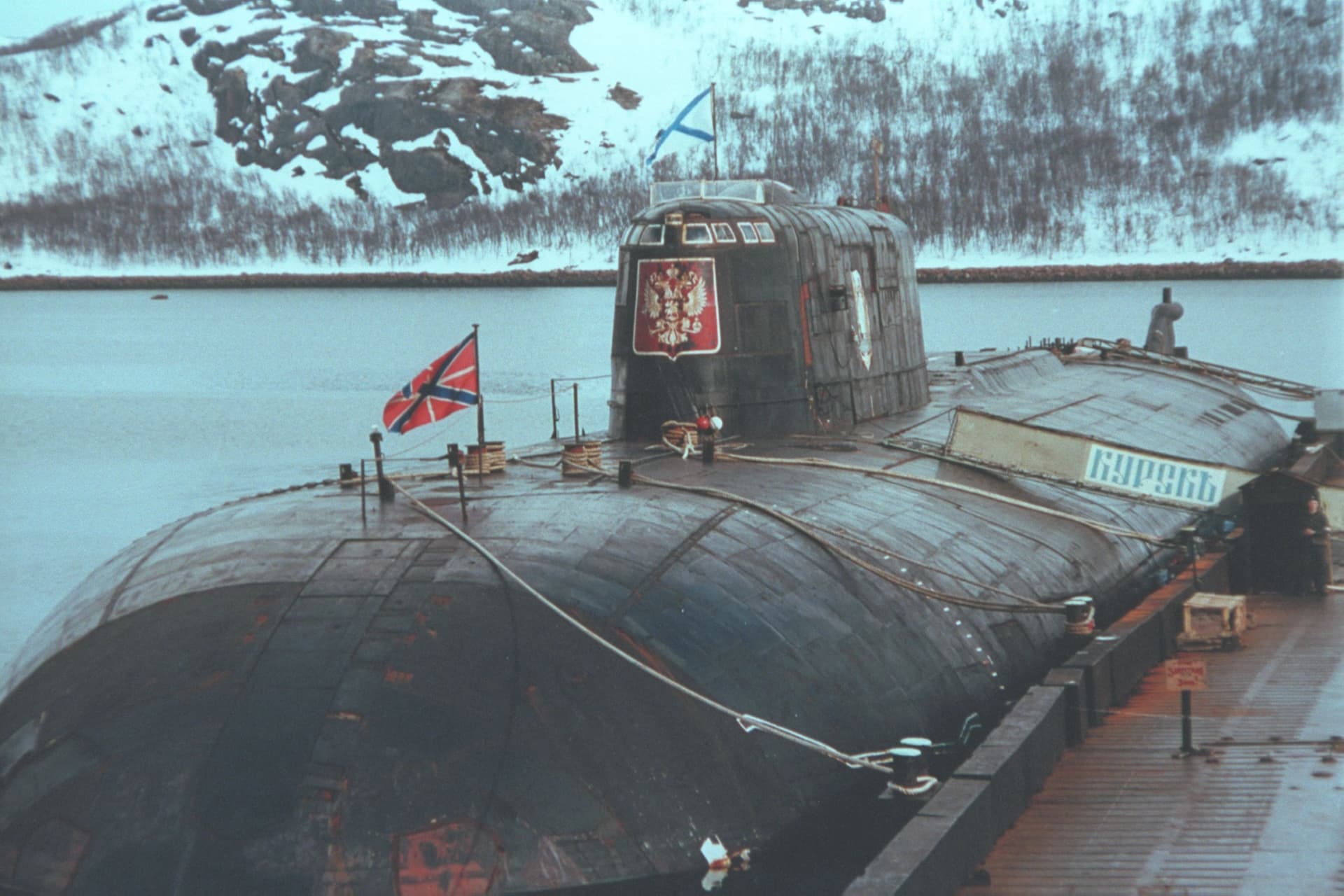

The submarine was named Kursk after the Battle of Kursk: the large-scale engagement between the forces of Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, known as the largest tank battle in history resulting in a Soviet victory. Kursk, which gave the battle its name, is a small city of 450.000 people and an administrative centre of the Kursk region.
It was launched in 1994, as a part of Russia's Northern Fleet. The fleet suffered major funding cutbacks throughout the 1990s. This led to poor upkeep of their equipment, including submarines. Many Northern Fleet sailors had also gone unpaid.
The submarine had somewhat of a mythical status of an “unsinkable submarine” as summarized in an article by Guardian. It was claimed that it could whitstand a direct hit from a torpedo. For this reason, it had the privilege to carry actual weapons even during the naval exercises.
In her five-year tenure, Kursk undertook just a single mission—a six-month deployment to the Mediterranean Sea in the summer of 1999. This mission involved monitoring the United States Sixth Fleet's response to the Kosovo crisis. As a result, many of her crew had spent little time at sea and were inexperienced.
In August 2000, the Kursk submarine participated in the “Summer-X” naval exercise—a significant event for the Russian Navy after over a decade. During this exercise, Kursk was equipped with live combat weapons, a privilege granted to only a few vessels. On the first day, it successfully launched a Granit missile with a dummy warhead (as a part of the exercise). However, tragedy struck two days later.
On August 12, 2000, while preparing to fire dummy torpedoes at the Kirov-class battlecruiser Pyotr Velikiy (as part of the naval exercise), an explosion occurred. The submarine sank after the explosion, in relatively shallow waters. All 118 personnel on board died—95 of them immediately, 23 approximately 6 hours later.
Explosion of the submarine was detected almost immediately, but the surrounding ships thought it to be a part of the exercise. For this reason, the rescue mission started only 6 hours after the explosion.
The British and Norwegian navies offered assistance, but the Russian government refused. Minister of Defence Igor Sergeyev claimed that the rescue was well underway. Vladimir Putin authorised the Russian Navy to accept the help only 5 days after the incident.
Russian and Norwegian divers found 23 bodies in the ninth compartment. It is believed that those crew members survived the initial explosion and were hiding in the wreckage for up to 6 hours. All of them ultimately died either by burning to death or of suffocation.
The army initially provided multiple versions of what caused the accident. Fleet Admiral Vladimir Kuroyedov said that Kursk collided with the foreign NATO vessel without providing evidence. This claim was supported by Russian Navy commanders for over two years, fueled by those seeking strained Russia-West relations.
Ultimately the official investigation found a technical fault to be the cause - a leak of highly concentrated hydrogen peroxide in the torpedo's casing—as reported by independent media worldwide (BBC, for example). Geophysicists and torpedo designers later supported this version of events.
Vice-Admiral Valery Ryazantsev blamed the systemic problems in the Russian army. He said poor training, maintenance, and inspections led to mishandling the weapon. A burned safety instruction copy found in the wreckage wasn't relevant to the torpedo. Kursk's crew lacked experience and training with HTP torpedoes. Inadequate inspections led to faulty actions. Ryazantsev believes these factors caused the explosion.
The Russian Navy initially downplayed the incident, the official search was ordered only 9 hours after the explosion. The rescue attempt process was somewhat urged by the relatives of the crew members, as the rumours of technical issues with the submarine started to spread among the community.
The first official announcement happened 2 days after the explosion, on 14 August. The media were informed that the submarine descended to the ocean floor, but:
All of those claims were proven false later, as there were no survivors left 6 hours after the explosion.
At the time of the incident, Vladimir Putin was shown on TV to enjoy his holiday in a seaside resort in Sochi. Despite his being informed immediately on the disaster, he only returned after 5 days. He later commented on the matter:
I probably should have returned to Moscow, but nothing would have changed. I had the same level of communication both in Sochi and in Moscow, but from a PR point of view I could have demonstrated some special eagerness to return.
BBC Europe
Another memorable moment was Vladimir Putin's interview on CNN with Larry King. When he was asked what happened to the submarine, he simply replied “She sank”. Many Russians remember this statement as a symbol of the disattached reaction to the disaster.
Media and the general public were extremely critical of this. Images of angry family members demanding information or waiting anxiously at the dock for news were shown in the media worldwide. It was a PR disaster for Vladimir Putin: his highly favourable ratings dropped dramatically.
Boris Kuznetsov, the lawyer of the families of 55 men onboard, sees the tragedy as a turning point for modern Russia. The Russian government, military and Vladimir Putin never took responsibility, according to him. Kuznetsov currently resides in the United States under a political asylum, because the Russian government issued an international arrest warrant for him.
The role of the Russian army is crucial in state propaganda. World War II is referred to as the Great Patriotic War, where the Soviet forces saved the entire world from fascism (for the great personal sacrifice of the general Russian population). This glorification is manifested in commemorations, parades, and cultural events that honour the wartime achievements and resilience of the nation.
A famously grotesque example of this is the Cathedral of the Russian Armed Forces— an enormous church built near Moscow with a metallic facade in the shade of khaki colour.
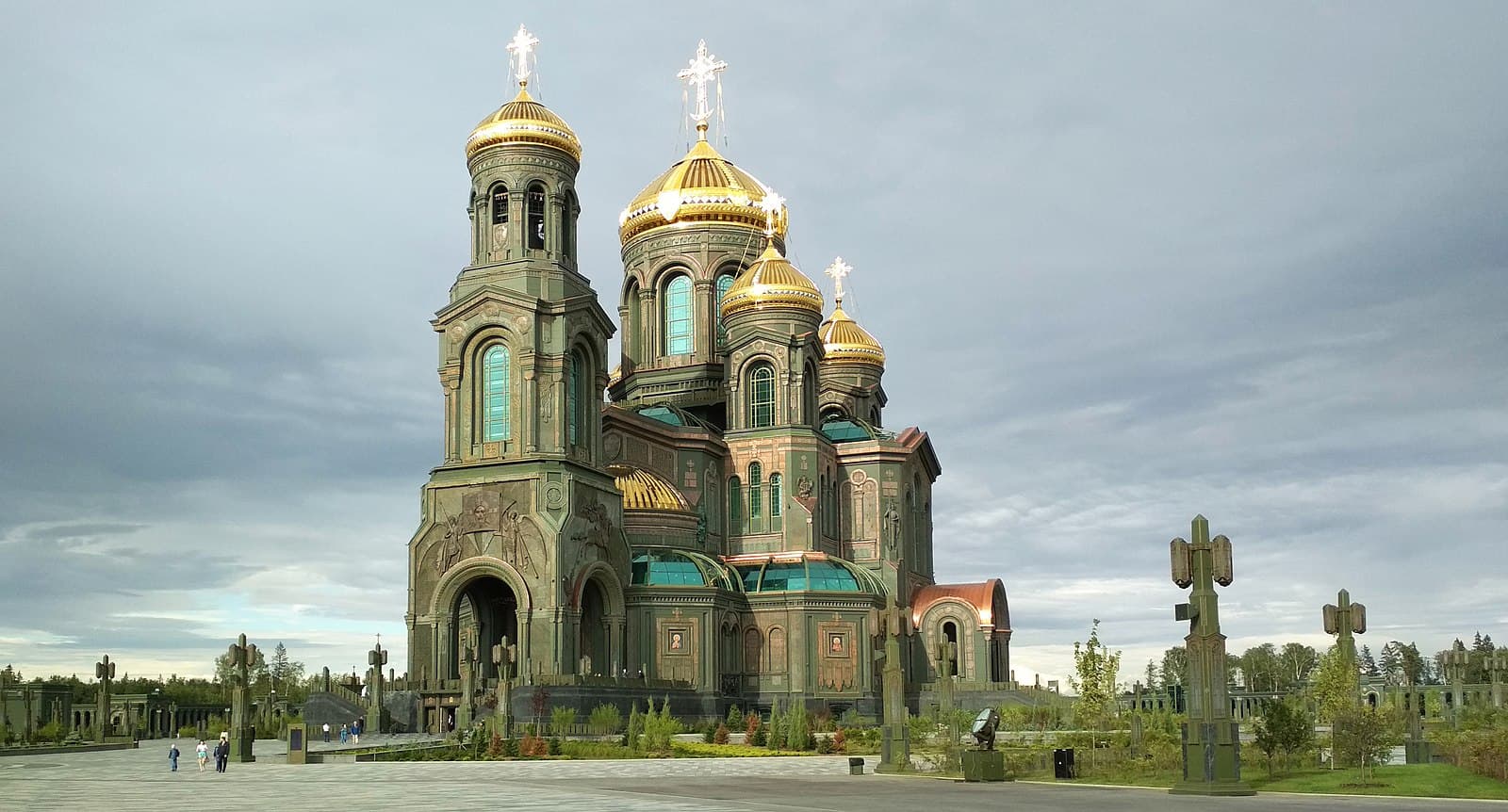

The praise of the army serves also as a convenient excuse to tighten the laws prohibiting freedom of speech: one of the major laws targeting freedom of speech is claiming to protect the armed forces from “discreditation” (read our article on this: “Discrediting” the armed forces).
Despite its status in the Russian propaganda narratives, the army faces a multitude of issues. Few examples:
The Russian invasion of Ukraine is, unfortunately, still an unfinished story. The Kursk disaster, however, is a well-explored moment in history. As such, we can use it to better understand the actual reality of the relationship between the Russian government and its army.
Dieser Artikel wurde noch nicht ins Deutsche übersetzt. Wir suchen nach Freiwilligen, die uns dabei helfen können.
Short biography of the freedom that never happened.

...Gebt nicht auf und verzweifelt nicht, tut, was ihr für richtig haltet. Russland wird auf jeden Fall frei sein.

Wie erklärt man die Unterstützung für Russland in der deutschen Politik?
Unsere Medienplattform würde ohne unser internationales Freiwilligenteam nicht existieren. Möchten Sie eine_r davon werden? Hier ist die Liste der derzeit offenen Stellen:
Gibt es eine andere Art wie Sie uns unterstützen möchten? Lassen Sie es uns wissen:
Wir berichten über die aktuellen Probleme Russlands und seiner Menschen, die sich gegen den Krieg und für die Demokratie einsetzen. Wir bemühen uns, unsere Inhalte für das europäische Publikum so zugänglich wie möglich zu machen.
Möchten Sie an den Inhalten von Russen gegen den Krieg mitwirken?
Wir wollen die Menschen aus Russland, die für Frieden und Demokratie stehen, gehört werden lassen. Wir veröffentlichen ihre Geschichten und interviewen sie im Projekt Fragen Sie einen Russen.
Sind Sie eine Person aus Russland oder kennen Sie jemanden, der seine Geschichte erzählen möchte? Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns. Ihre Erfahrungen werden den Menschen helfen zu verstehen, wie Russland funktioniert.
Wir können Ihre Erfahrungen anonym veröffentlichen.
Unser Projekt wird von internationalen Freiwilligen betrieben - kein einziges Mitglied des Teams wird in jeglicher Weise bezahlt. Das Projekt hat jedoch laufende Kosten: Hosting, Domains, Abonnements für kostenpflichtige Online-Dienste (wie Midjourney oder Fillout.com) und Werbung.




Russland hat den Krieg gegen die Ukraine angefangen. Dieser Krieg dauert schon seit 2014 an. Er hat sich seit 24. Februar 2022 nur noch verschärft. Millionen von Ukrainern leiden. Die Schuldigen müssen für ihre Verbrechen zur Rechenschaft gezogen werden.
Das russische Regime versucht, die liberalen Stimmen zum Schweigen zu bringen. Es gibt russische Menschen, die gegen den Krieg sind - und das russische Regime versucht alles, um sie zum Schweigen zu bringen. Wir wollen das verhindern und ihren Stimmen Gehör verschaffen.
**Die russischen liberalen Initiativen sind für die europäische Öffentlichkeit bisweilen schwer zu verstehen. Der rechtliche, soziale und historische Kontext in Russland ist nicht immer klar. Wir wollen Informationen austauschen, Brücken bauen und das liberale Russland mit dem Westen verbinden.
Wir glauben an den Dialog, nicht an die Isolation. Die oppositionellen Kräfte in Russland werden ohne die Unterstützung der demokratischen Welt nichts verändern können. Wir glauben auch, dass der Dialog in beide Richtungen gehen sollte.
Die Wahl liegt bei Ihnen. Wir verstehen die Wut über die Verbrechen Russlands. Es liegt an Ihnen, ob Sie auf das russische Volk hören wollen, das sich dagegen wehrt.